NapaJen’s Target Delivery Technology
NapaJen’s novel, proprietary delivery vehicle is built upon schizophyllan glucan (SPG) that specifically binds to Dectin-1, a cell surface receptor expressed on antigen presenting immune cells, such as dendritic cells and macrophages/monocytes. By complexing oligonucleotides with schizophyllan, NapaJen’s delivery platform uniquely enables the efficient and selective delivery of oligonucleotides to cells playing key roles in regulating immune responses.
Development of an Oligonucleotide-SPG Complex
The development of NapaJen’s proprietary oligonucleotide complexes is achieved by:
- Denaturation of the triple helix SPG into single strands
- Bonding of a polydeoxyadenine (poly[dA]) extension to the selected oligonucleotide drug
- Addition of the select oligonucleotide drug with its poly(dA) extension to the single stranded SPG mixture
- Renaturation of the SPG strands into its natural triple helix form, which now includes the selected oligonucleotide.
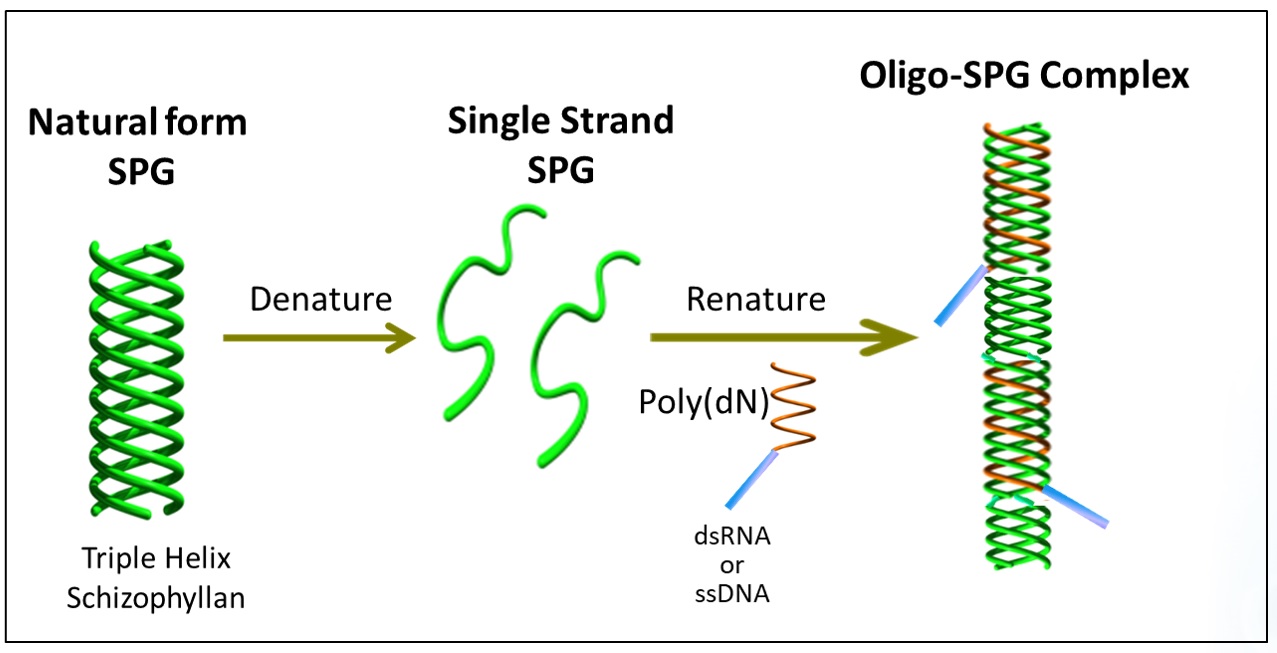 Fig. 4. Development of the oligo complex.
Fig. 4. Development of the oligo complex.
Targeted Delivery Approach Utilizing an Oligonucleotide-SPG Complex
Dectin-1, which serves as a receptor for SPG, is predominantly expressed throughout the body on immune cells such as macrophages/monocytes and dendritic cells. As such, when complexed with SPG, an oligonucleotide is able to be selectively delivered to those Dectin-1 positive immune cells.
Once the oligonucleotide-SPG complex is delivered to the target cell, the oligonucleotide is taken up by intracellular endosomes and subsequently enters the cytoplasm.
Once inside the cell, the action of the oligonucleotide depends on its type:
TLR9 Agonist Oligonucleotide: Binds to TLR9 in the endosome to induce cytokines such as interferon-alpha
Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA) Oligonucleotide: After escaping the endosome, the guide strand is incorporated into RISC and binds to target mRNA to induce cleavage.
Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA) Oligonucleotide: Binds directly to the target mRNA and induces cleavage of the target mRNA by RNase H.
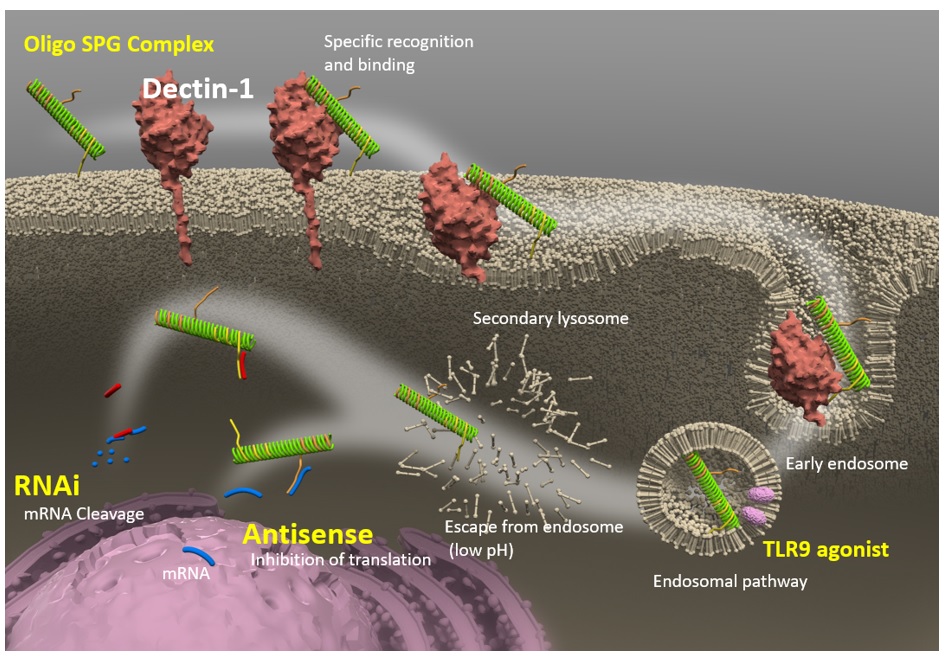 Fig. 3. Fig. 4 shows a schematic illustration of the uptake and journey of the oligo-poly(dA)/SPG complex in Dectin-1 expressing cells.
Fig. 3. Fig. 4 shows a schematic illustration of the uptake and journey of the oligo-poly(dA)/SPG complex in Dectin-1 expressing cells.
Based on NapaJen’s evaluation of its delivery technology to date, we believe that the key advantages of our oligonucleotide-SPG complex delivery approach include:
- Efficient delivery of oligonucleotide drugs to target cells
- Advantageous safety profile highlighted by demonstrated lack of toxicity at highest doses evaluated in non-human primate studies, as well as ongoing first-in-human clinical trial.
- Opportunity to address a broad range of therapeutic indications
